The material contained here is "FOR INFORMATION ONLY" and should not replace the counsel and advice of your personal physician. Promptly consulting your doctor is the best path to a quick and successful resolution of any medical problem.
Free contribution
WELCOME
Antonio Marin S.
P.O. Box,173
07080 Palma
Spain

Cholesterol terms 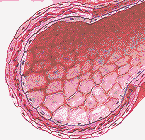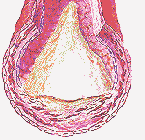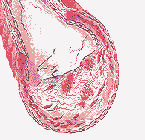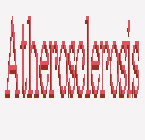
When reading about cholesterol and nutrition, you
may run across some words that are important to
understand if you are trying to fully grasp the meaning
of the articles you are studying.
This glossary may be used to help clarify the meaning and
use of important words used in material on the subject of
cholesterol.
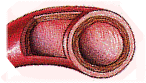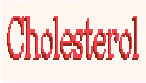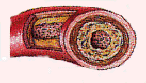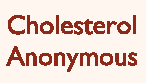
ATHEROSCLEROSIS: Essentially a type of hardening of the arteries; it's a condition in which the walls of the arteries become less flexible because of the buildup of cholesterol, fat and other blood components within them. Arteries to the heart may narrow due to atherosclerosis and become incapable of carrying enough oxygen-rich blood to the muscles of the heart.
CARBOHYDRATE:
One of the three types of
nutrients (along with fat and protein) that provide
energy to the body.
There are four calories in each gram of carbohydrate, an
essential ingredient for normal body function.
There are two basic types of carbohydrates:
"simple" carbohydrates (sugars), and
"complex" carbohydrate (starches and fiber).
Complex carbohydrate: Starch and fiber, usually found in plants or vegetables. When complex carbohydrates are substituted for saturated fats in the diet, the saturated fat reduction lowers blood cholesterol. High amounts of starch may be found in breads, pasta, rice, cereals, dried beans and peas, corn and lima beans.
Fiber: The body i unable to digest or absorb this type of complex carbohydrate, so high-fiber foods are low in calories. Large amounts of fiber are found in whole-grain cereals, oat and barley brans, some fruits such as apples and oranges, as well as dried beans.
CHOLESTEROL:
A soft, waxy substance that is important for normal body function and is produced in sufficient quantity by the body. It is involved in the production of certain hormones, bile acid and Vitamin D. It may be found in tissues in all parts of the body, including the nervous system, muscle, skin, heart, intestines and liver.
Blood Cholesterol: May be from both cholesterol absorbed from food and cholesterol produced in the liver, it is distributed to tissues throughout the body by the blood. A high level of blood cholesterol precedes the development of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease.
Dietary Cholesterol: The amounts of cholesterol contained in the foods you consume. It is present only in foods derived from animals, and is not contained in foods that are of plant origin.
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: A disease of the arteries of the heart. The arteries become narrower due to the effects of arteriosclerosis, and fail to provide sufficient amounts of oxygen and nutrient-carrying blood to the tissues (muscles) of the heart, leading to chest pain, heart attack and death.
FAT:
One of the three types of nutrients, fat provides nine calories per gram, more than twice the amount contained in an equal quantity of either carbohydrates or proteins. Fats help in the absorption of certain vitamins and, in small amounts, are necessary for normal body function.
Total Fat: The total of all types of fats (saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated) contained in food. In general, a mixture of all three is found in most foods.
Saturated Fat: This type of fat is found in the largest amounts in foods derived from animals, including meat, poultry, and dairy products made from milk, such as cream, cheese, ice cream and butter. However, some vegetable oils, including coconut, palm kernel and other palm oils, also contain large amounts of saturated fats. Blood cholesterol increases more from saturated fats than any other food element in the diet.
Unsaturated Fat:
This type of fat remains in a liquid state at
refrigerator temperatures. Both monounsaturated and
polyunsaturated fats are in this classification.
Monounsaturated Fat: This is a type of fat that is
slightly unsaturated and is contained in foods made from
plants, including olive oil and canola (rapeseed oil).
When these types of fats are substituted for saturated
fats in the diet, blood cholesterol is reduced.
Polyunsaturated Fat: Considered highly unsaturated, this type of fat is found in oils made from safflower, sunflower, corn and soybean. It also acts to reduce the amount of blood cholesterol when substituted for saturated fats in the diet.
GRAM:
A unit of weight. One ounce equals about 28 grams (g). Most diets measure the various contents of food products using this unit of weight.
HYDROGENATION:
A chemical process that changes liquid vegetable oils that are made of unsaturated fats, into a solid form that contains saturated fats. While this process makes it possible to keep these products on supermarket shelves for longer periods of time, it also increases the content of undesirable saturated fats.
LIPIDS:
These are fatty substances that are present in the blood and body issues, and includes cholesterol and triglycerides.
LIPOPROTEINS:
Used to describe the protein-coated "packages" or particles that carry fats (such as cholesterol) through the blood. Lipoproteins are classified according to their density.
High Density Lipoproteins (HDL): This form of lipoprotein contains a small amount of cholesterol and carries cholesterol away from the body cells and tissues to the liver for excretion from the body. Thus, the higher the level of HDL the better, and so this substance is known as the "good" cholesterol.
Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL): These are the lipoproteins in the blood that carry the largest amounts of cholesterol. Because LDL is responsible for depositing cholesterol in the walls of arteries, high levels are associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease. This is the substance referred to as "bad" cholesterol.
MILLIGRAM:
A unit of weight equal to one-thousandth of a gram. One ounce equals 28,350 milligrams (mg).
MILLIGRAMS/DECILITER (mg/dl):
This unit is used to express the concentration of a given weight of a substance dissolved in a quantity of liquid. The amount of cholesterol in the blood is measured in this manner, indicating the weight of cholesterol (mg) in a deciliter of blood. A deciliter is about one-tenth of a quart.
PROTEIN:
One of the three types of nutrients. One gram or protein supplies four calories, less than half the amount contained in one gram of fat. Protein is an essential building block of many parts of the body, including muscle, bone, skin and blood.
RISK FACTOR: A habit, trait or condition in a person that is associated with an increased chance of developing a particular disease. These factors are established by studying the results of many clinical investigations that develop the statistics needed to discover the relationships.
TRIGLYCERIDES: A type of lipid (fat-like substance) carried in the bloodstream to the tissues. Most of the body's fat tissue is in this form, stored for use as energy. Triglycerides are obtained from the fat in the diet.
VASCULAR DISEASE:
A disease or ailment of the blood vessels, frequently caused by atherosclerosis. Vascular disease may be seen in arteries to the brain, heart and in the leg.
Last Updated:
May 1, 2000
